Galvanized Steel Sheet
What is Galvanized Steel?
Galvanized steel is a high-quality construction material widely used in various industries and building projects. It is produced by coating the surface of steel with a layer of corrosion-resistant zinc, providing superior advantages compared to regular steel. Galvanized steel with thicknesses of 1mm and 2mm creates products with different technical properties, meeting the diverse demands of the market.

Advantages of Galvanized Steel
- Durable and corrosion-resistant: The zinc coating protects the surface of the steel from the influence of the external environment, from harsh climates to corrosive chemicals. This extends the lifespan and maintains the durability of galvanized steel over time.
- High strength in harsh conditions: Thick galvanized steel has the ability to withstand force, impact, and pressure from wind, storms, or heavy loads. This makes it an ideal material for construction projects that require stability and high safety.
Technical Properties of Galvanized Steel
Galvanized steel is a construction material with special technical properties, making it a popular and preferred choice in building and industrial applications. The following are some important properties of galvanized steel:
Density of Galvanized Steel
Density is one of the important characteristics of materials. In the case of galvanized steel, the density typically ranges from 7,000 to 8,050 kg/m³. This means that galvanized steel is relatively heavy, depending on the thickness and size of the sheet. The high density of galvanized steel plays an important role in determining its weight and maximum load capacity in construction applications.
Size of Galvanized Steel
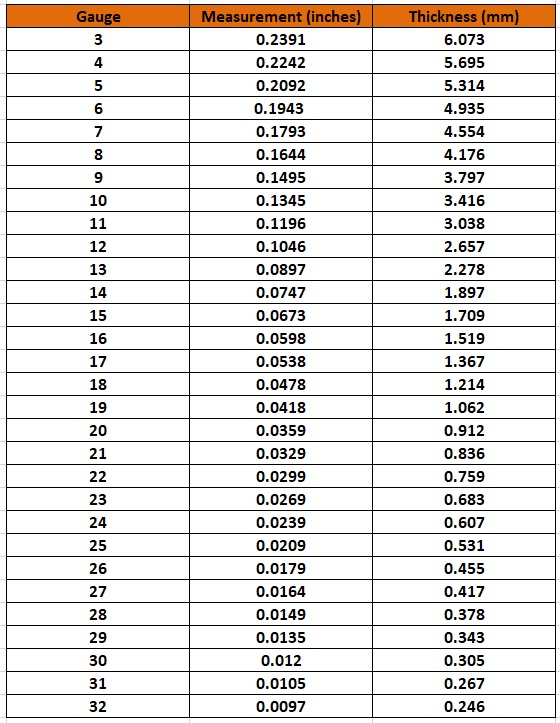
Galvanized steel comes in various sizes and thicknesses, suitable for various applications. Typically, the thickness of galvanized steel can range from 0.12mm to 4.0mm, but the most common thicknesses are usually between 0.4mm to 1.5mm. For industrial and construction applications, galvanized steel usually has a width ranging from 600mm to 1250mm. However, customized galvanized steel with specific sizes and thicknesses can be produced based on the customer’s requirements.
Mechanical Strength
Galvanized steel has high mechanical strength and can withstand forces and pressures effectively. This makes it an ideal material for use in constructions requiring stability and safety, such as warehouses, workshops, and building structures.
Corrosion Resistance
One of the prominent advantages of galvanized steel is its excellent corrosion resistance. Thanks to the zinc coating protecting the surface of the steel, galvanized steel can resist corrosion from harsh weather, chemical factors, and wet environments.
Lifespan and Preservation
Galvanized steel has a long lifespan and requires little effort to maintain. Its corrosion-resistant properties help prolong the lifespan of the product, reducing maintenance and replacement costs.
These technical properties make galvanized steel an ideal material for building and industrial applications. Galvanized steel offers superior mechanical properties and good corrosion resistance, enhancing the performance and durability of constructions and products.

Galvanized Steel Standards
Galvanized steel standards are technical specifications and regulations established to ensure the quality and technical properties of galvanized steel produced and used properly. These standards are usually determined and issued by local or international organizations and government agencies.
Some common international standards related to galvanized steel include:
- ASTM A653 / A653M: The standard of the American Society for Testing and Materials (ASTM) for continuously galvanized steel, continuously galvanized alloy steel, or continuously galvanized alloy steel sheets after welding.
- EN 10346: The European standard for continuously hot-dip coated steel sheet and strip applied for continuously hot-dip coated galvanized steel and continuously hot-dip coated galvanized steel sheets after welding.
- JIS G3302: The standard of the Japanese Industrial Standards (JIS) for continuously hot-dip galvanized steel sheet and strip.
- ISO 3575: The international standard of the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) for continuously hot-dip zinc-coated steel sheet and coil.
Galvanized Steel Pricing
Currently, there are many manufacturers and suppliers providing galvanized steel with various thicknesses and sizes. To obtain pricing for galvanized steel with thicknesses of 1mm and 2mm, you should contact the suppliers directly to receive specific information and reasonable prices.
For more information or to discuss your acrylic needs, contact us at:
Abu Taher: 99607244 / 98033712
Huzaifa Soni: 95598492
Or email us at sales@honeststeelkw.com to speak with our team directly.
Galvanized Steel Production Process
The galvanized steel production process includes two main stages: surface preparation and cleaning, and zinc coating on the steel. To ensure high quality and reliable corrosion resistance of galvanized steel, both stages are crucial and require accuracy and high technical standards.
Surface Preparation and Cleaning
This is the first and most important step in the galvanized steel production process. The goal of this stage is to clean the steel surface and remove rust, grease, and other contaminants to prepare for the next zinc coating process.
The steps involved are as follows:
a. Contaminant removal: The steel is passed through pickling tanks to remove dirt, grease, and other impurities from the surface. The pickling process is quick and efficient, ensuring that the zinc coating adheres firmly to the steel surface.
b. Sandblasting (if needed): For steel with heavy rust or requiring polishing, sandblasting is performed to clean the steel and prepare the surface for galvanizing.
c. Acid treatment: In some cases, acid may be used to clean the steel surface in detail and remove difficult contaminants.

Zinc Coating on the Steel
After the steel surface is thoroughly cleaned, the zinc coating process will be carried out. Zinc coating is the process of applying a layer of molten zinc, which provides a strong zinc coating firmly adhered to the steel surface through either electroplating or hot-dip coating methods.
The steps involved are as follows:
a. Electroplating: The steel is passed through a zinc solution tank. The use of electric current promotes a chemical reaction between the steel and zinc, resulting in a firm zinc coating on the steel surface. This method is common for galvanizing small and complex details.
b. Hot-dip coating: The steel is passed through a molten zinc bath at a high temperature, where the zinc melts and forms a firm zinc coating on the steel surface. This method is often used to galvanise large sheets or sheets of special sizes and shapes.
After the zinc coating stage is completed, galvanized steel is carefully inspected to ensure that the quality and technical properties meet the standards. Galvanized steel that has undergone this production process will have excellent corrosion resistance and durability, effectively serving the purpose of construction and industry.
Considerations When Using Galvanized Steel
There are several considerations to ensure its corrosion resistance and good performance during use when using galvanised steel. The following are important points to consider when using galvanized steel:
Proper storage and transportation:
During transportation and storage, galvanized steel should be handled with care to avoid breakage, scratches, or surface damage. In particular, avoid contact with chemicals and strong mechanical impacts that can damage the zinc coating and reduce the corrosion resistance of the steel.
Product quality check:
Before use, thoroughly inspect the galvanized steel to ensure its technical properties and durability. Check the surface of the steel for any defects, scratches, or abnormalities. If any issues are found, promptly inform the supplier or manufacturer to receive support and address the issue.
Proper installation and connections:
When installing galvanized steel, use proper installation methods and ensure that the connections, screws, and fasteners used are made of materials compatible with galvanized steel. Using stainless steel screws and accessories will reduce the risk of electrochemical corrosion and corrosion.
Follow standards and guidelines:
Adhere to the technical standards and guidelines provided by the manufacturer or relevant government agencies when using galvanized steel. These guidelines include regulations on thickness, installation methods, preservation, and maintenance of the product.
Regular maintenance:
To maintain the corrosion resistance and lifespan of galvanized steel, perform regular maintenance. This includes checking and cleaning the galvanized steel surface, repainting scratched areas, and replacing damaged or aged parts.
Prevent electrochemical interaction:
When using galvanized steel alongside other metals, avoid direct contact between different metals, especially when they are wet or in a moist environment. Electrochemical interaction between different metals can cause corrosion and damage the zinc coating.
Customize warranty policies:
If you plan to use galvanized steel in special applications or have specific requirements, customize the warranty policies with the supplier or manufacturer. This ensures that the product meets your specific requirements and quality.
By paying attention to and following the requirements and advice above, you can effectively and durably use galvanized steel, ensuring its corrosion resistance and durability over time.

Conclusion
Galvanized steel is an important construction material with numerous superior advantages. With its corrosion resistance and high durability, galvanized steel has been widely used in various industrial and construction fields. Choosing and using the appropriate galvanized steel with thicknesses of 1mm or 2mm for each specific application is crucial to ensure efficiency and safety in construction projects.